
- #METAL ION REACTIVITY SERIES SERIES#
- #METAL ION REACTIVITY SERIES FREE#
In these reactions, a free element displaces another element from its compound, producing a new compound.
Some metals react with acid and replace hydrogen from the acid.Ī single displacement reaction is an important type of chemical reaction. Metals react with oxygen in the air to form oxides. The most reactive metals will react even water, while the least reactive metals will not react even with acid.Įxample: If we put a small piece of sodium metal in water, sodium reacts exothermically with water producing hydrogen and metal hydroxide. A more reactive metal readily reacts with other elements. Metals exist in solid state at room temperature except for mercury, which is in a liquid state at room temperature. In most metals, the atoms are highly close packed, so they have high density.  They are malleable and ductile, so they can be bent and stretched without breaking.
They are malleable and ductile, so they can be bent and stretched without breaking.  Good conductors of heat and electricity: In metals, the positive ions are surrounded by a sea of electrons and these are responsible for their conductivity. Now, let’s explore the properties of metals… A diagonal line from boron to polonium separates metals from non-metals. Non-metallic elements occupy the right side of the periodic table. These are also metallic in nature and are called transition metals. Elements of group 3 to 12 are transition elements. Group1 and group 2 elements are together called s-block elements. Alkaline earth metals are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg) calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba) and radium (Ra). The group 2 elements in the periodic table are called alkaline earth metals. Alkali metals are lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs) and francium (Fr). Alkali metals comprise group 1 in the periodic table along with hydrogen.
Good conductors of heat and electricity: In metals, the positive ions are surrounded by a sea of electrons and these are responsible for their conductivity. Now, let’s explore the properties of metals… A diagonal line from boron to polonium separates metals from non-metals. Non-metallic elements occupy the right side of the periodic table. These are also metallic in nature and are called transition metals. Elements of group 3 to 12 are transition elements. Group1 and group 2 elements are together called s-block elements. Alkaline earth metals are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg) calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba) and radium (Ra). The group 2 elements in the periodic table are called alkaline earth metals. Alkali metals are lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs) and francium (Fr). Alkali metals comprise group 1 in the periodic table along with hydrogen. The alkali metals are a series of chemical elements in the periodic table. Metals occupy the bulk of the periodic table. How are metals arranged in a periodic table? The more reactive a metal, the greater tendency it has to form a positive ion in a chemical reaction. Most metals are electropositive in nature and the metal atoms lose electrons in chemical reactions to form cations.
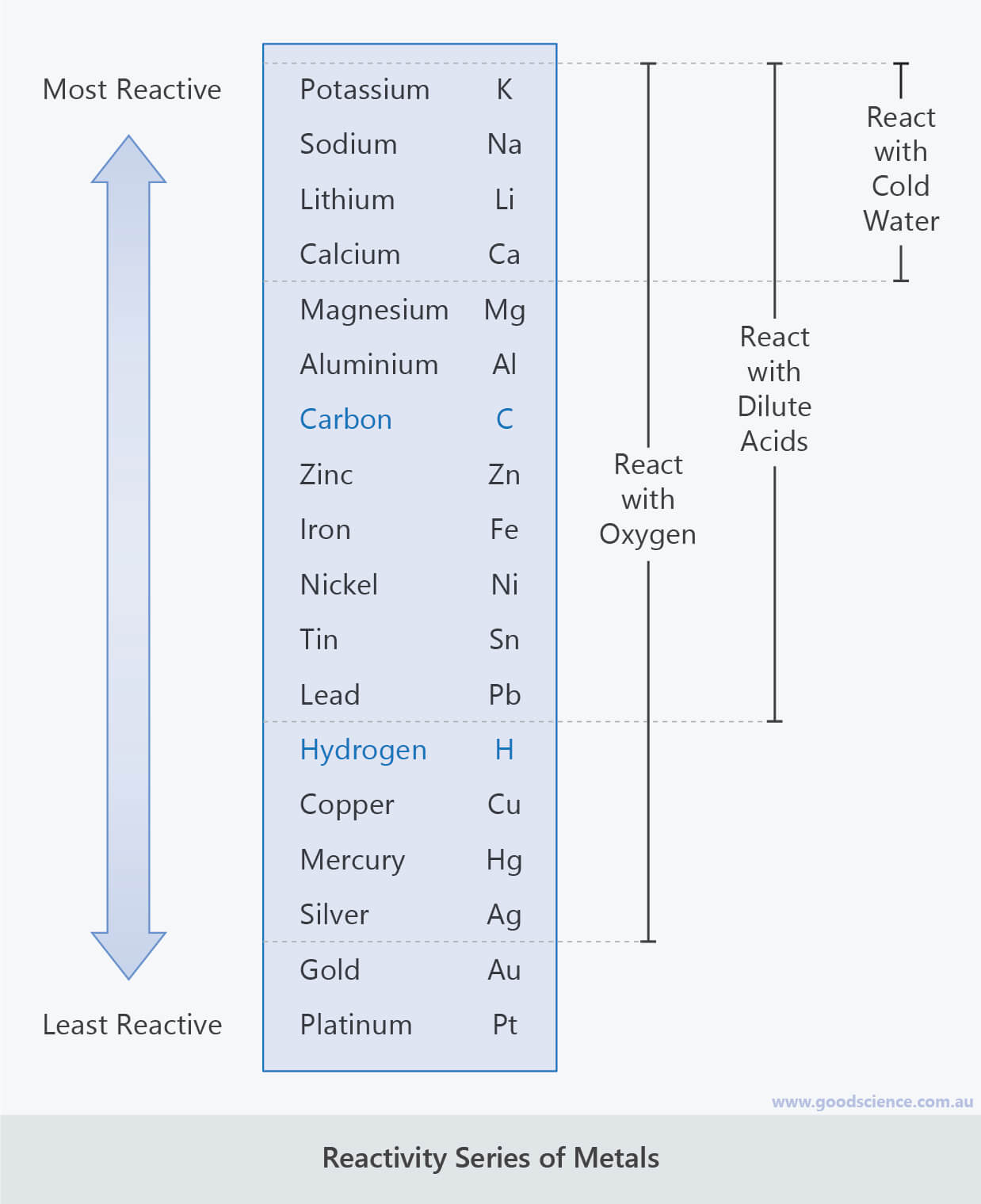
Metals are elements and are good conductors of heat and electricity. A more sophisticated calculation involving electrode potentials is required to make accurate predictions in this area.To observe the action of Zn, Fe, Cu and Al metals on the following salt solutions:Īrrange Zn, Fe, Cu and Al metals in the decreasing order of reactivity based on the above results. For example, calcium is quite reactive with water, whereas magnesium does not react with cold water but does displace hydrogen from steam. The boundary between the metals that react with water and those that don't is harder to spot. Those metals that can displace H + ions from acids are easily recognized by their position above H in the activity series. Less active metals like iron or zinc cannot displace hydrogen from water but do readily react with acids: Sodium is highly active and is able to displace hydrogen from water:

It is important to distinguish between the displacement of hydrogen from an acid and hydrogen from water. However, silver cannot displace copper ions from solution.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
